【印刷可能】 air sinuses in skull 102650-Air sinuses in skull
Ninja Nerds,Join us in this video where we discuss the anatomy of the sinus skull and go into detail on the different types of sinus cavities through the useFrontal sinus Outline of bones of face, showing position of air sinuses Frontal sinus is shown in green The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges Sinuses are mucosa lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull Each opens into the anterior part of the correspondingSinuses, also called paranasal sinuses, are airfilled spaces within the facial bones surrounding the nose The paranasal sinuses have several theorized purposes They lighten the skull and allow our voices to resonate better Functionally, they produce
What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities
Air sinuses in skull
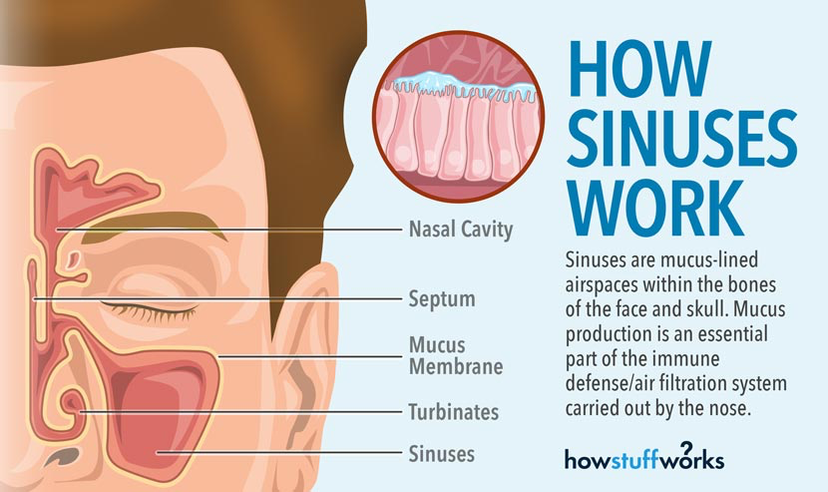
Air sinuses in skull-Yaw animation of the skull of a human (OUVC ), revealing the brain, nasal cavity, paranasal air sinuses, and middle ear sinuses Rendered in Amira, MayaThe sinuses lighten the skull or improve our voices, but their main function is to produce a mucus that moisturizes the inside of the nose This mucus layer protects the nose from pollutants, microorganisms, dust and dirt Click to see full answer
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10270/Paranasal_Sinuses.png)



Schwannoma Of The Nasal Cavity Clinical Case Diagnosis Kenhub
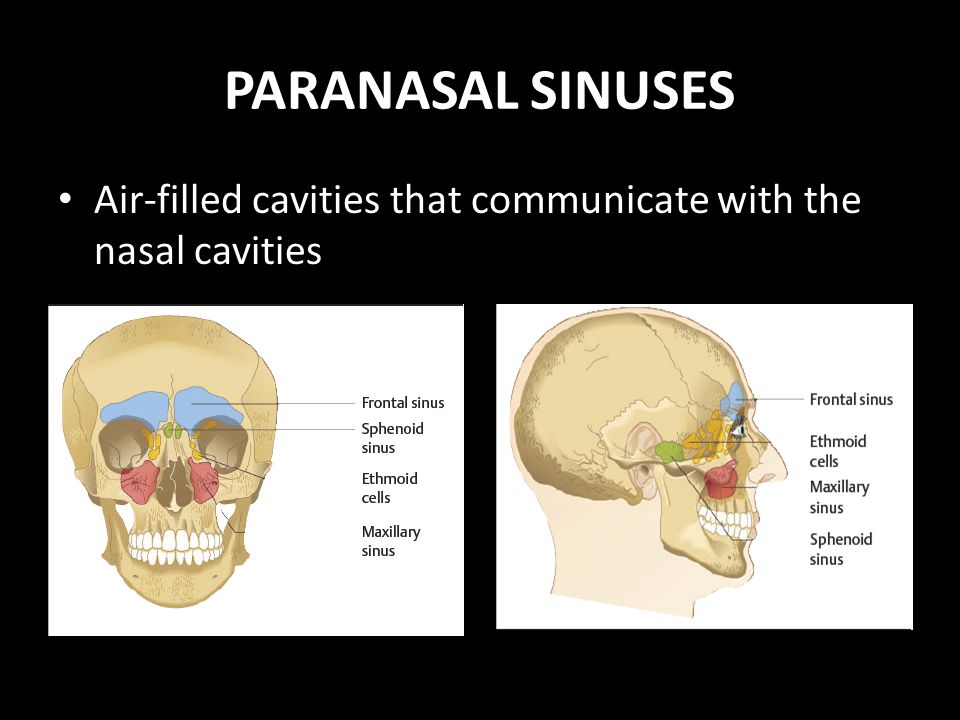
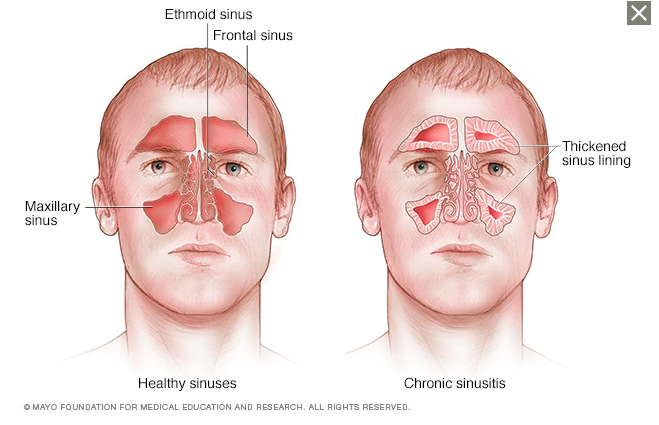
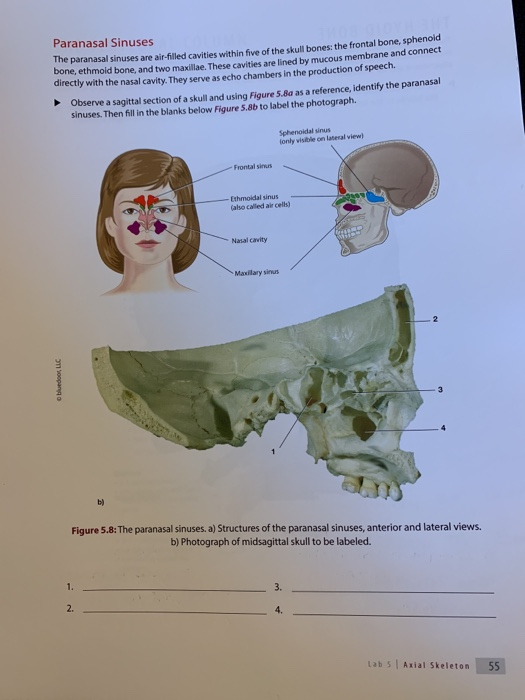
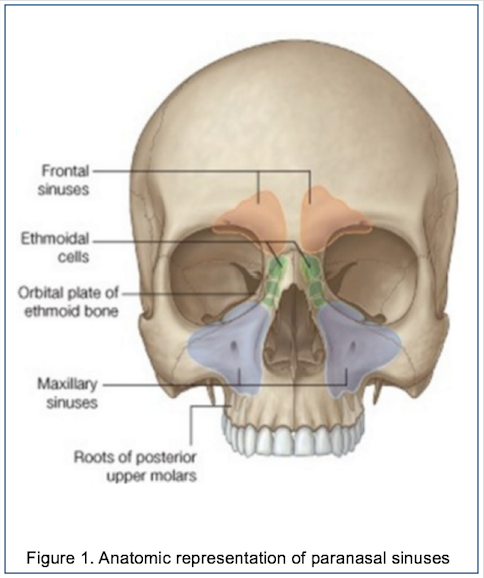
The paranasal sinuses are hollow, airfilled spaces located within certain bones of the skull (Figure 627) All of the sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity (paranasal = "next to nasal cavity") and are lined with nasal mucosa They serve to reduce bone mass and thus lighten the skull, and they also add resonance to the voice This second feature is most obvious when you have a cold orSinus and nasal cancer occurs in the mucusproducing tissues that line the nasal cavity (the space behind the nose through which air passes to the throat) and the paranasal sinuses (hollow areas in the facial bones near the nose) More than half of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers occur in the maxillary sinuses (hollow spaces on either side of the nose and below theAim The aim of this study is to measure the right and left maxillary and frontal air sinus dimensions and their application in age determination and gender identification Materials and Methods Twenty Posteroanterior (PA) skull radiographs were used for the study The width, length and distance across the right and left sinuses were measured using the Planmeca Romexis Viewer software
The sinuses are an airfilled cavity in a dense portion of a skull bone They actually decrease the weight of the skull The sinuses are formed in four rightleft pairs The frontal sinuses are positioned behind the forehead, while the maxillary sinuses are behind the cheeks The sphenoid and ethmoid sinuses are deeper in the skull behind the eyes and maxillary sinuses The sinuses · Sinuses of the face are cavities or spaces within the bones that help humidify the air and secrete mucus to help with air filtration Additionally, they contribute to the strength of the skull and its ability to resist traumaThe sinus cavities also allow more resonance to be added to the voice The sinuses are often referred to as the paranasal sinuses because of their location andTraumatic pneumocephalus in the context of trauma, sphenoid or skull base fracture needs to be excluded
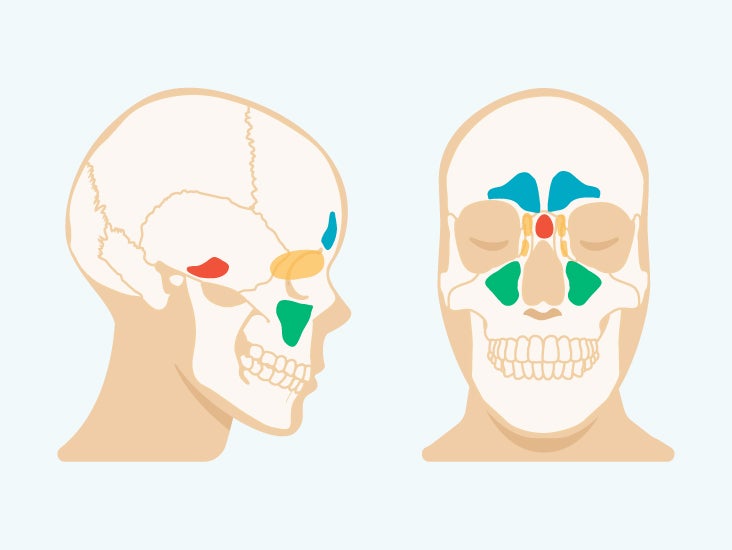
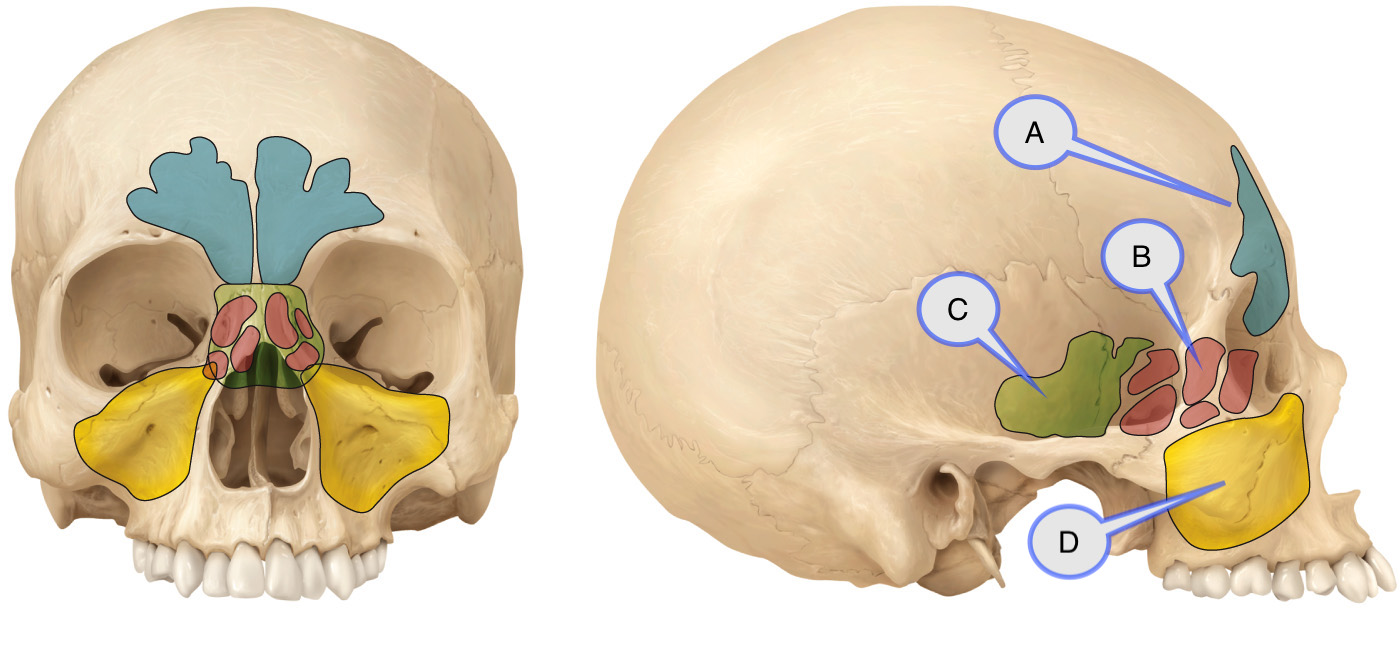
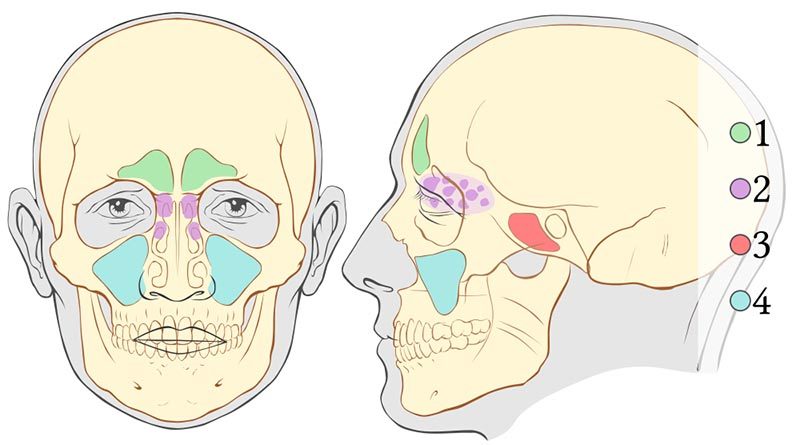
· Subtracting the volumes of the bony skull, air sinuses, and endocast from total head volume gives the volume of the remaining soft tissue To convert volumes to masses, volume (cm 3) was multiplied by density (g/cm 3) Ignoring the thin sinus epithelium, air sinus density was taken as zero, as was the resulting mass Density of the cranial endocast was assigned the density ofParanasal sinuses are a group of four paired airfilled spaces that surround the nasal cavity The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; · Sinuses are airfilled sacs (empty spaces) on either side of the nasal cavity that filter and clean the air breathed through the nose and lighten the bones of the skull




Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Lateral View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Anatomy Of Nose And Paranasal Sinus By The
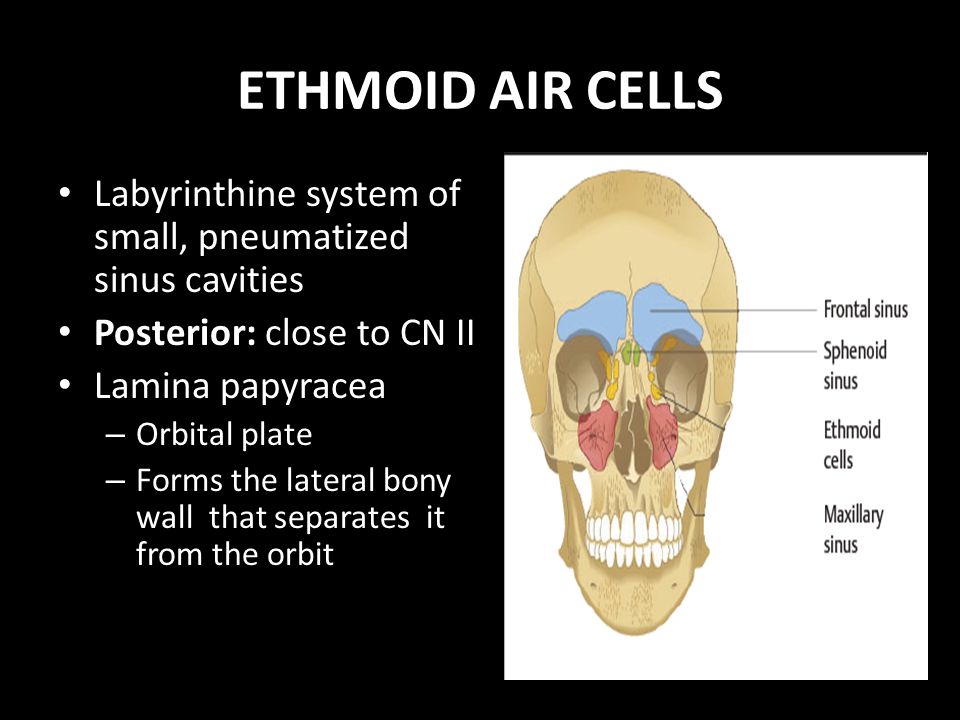
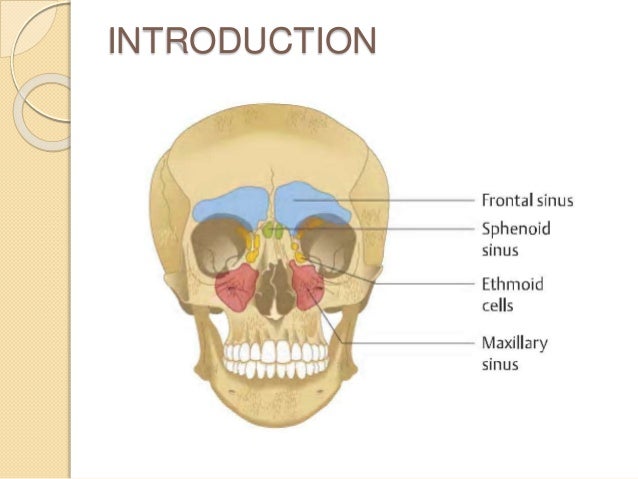
Frontal sinus, sphenoidal sinus,;Air Sinuses of the Skull Several of the bones of the skull have developed air spaces that are lined with mucous membrane It is this mucous membrane that becomes infected in sever cases of sinusitis It is also irritation of the mucous membrane that results in excessive fluid production that can fill the air spaces and give you a stuffed nose feeling Since these sinuses are embedded in0513 · There are two frontal sinuses located within the frontal bone of the skull They are the most superior of the paranasal sinuses, and are triangular in shape Drainage is via the frontonasal duct It opens out at the hiatus semilunaris, within the middle meatus of the nasal cavity




Sinusitis Of Human Skull With Inflamed At Sinus 3d Illustration Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Nose And Sinuses Amboss
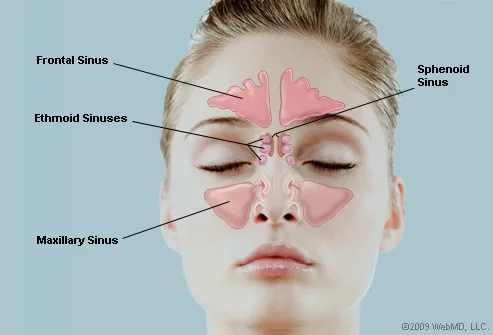
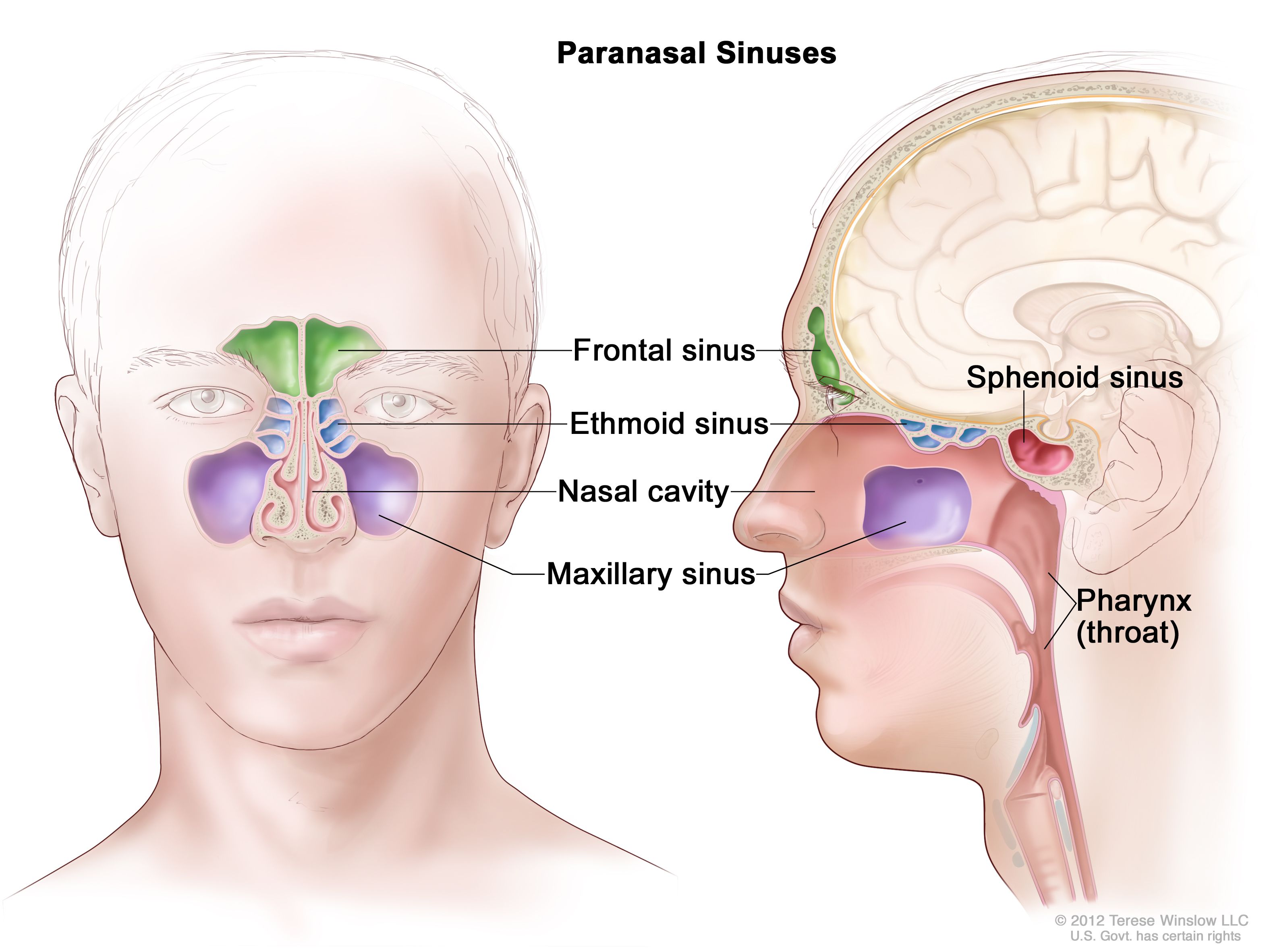
The bones of the face and skull near the nose contain four pairs of airfilled pockets, which are called the paranasal sinuses The paranasal sinuses include the following types of sinuses A maxillary sinus in each cheek Between six and 12 ethmoid sinuses on each side ofVentrally along the cetacean skull, connect the pharynx and middle ear cavities Mysticetes (baleen whales) have a large midline laryngeal sac Although cetacean air sacs do not appear to be homologous to paranasal sinuses, they may serve some analogous respiratory, vocal, or structural functions For example, these sacs may participate in gas exchange, thermoregulation,Air within cerebral venous sinuses need not always be due to septic thrombosis, skull fractures, nose blowing, rhinosinusitis, or barotrauma It can be iatrogenic through an intravenous access while intravenous medication or fluid is being injected Our case emphasizes the relevance of removing air bubbles completely and judiciously before starting an intravenous access




Tumours Of Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Col Shoaib



1
· This serves to moisten the air we breathe through our noses The hollow sinuses also act to lighten the bones of the skull and serve as resonating chambers forThe skull also contains sinuses, airfilled cavities known as paranasal sinuses, and numerous foraminaThe sinuses are lined with respiratory epitheliumTheir known functions are the lessening of the weight of the skull, the aiding of resonance to the voice and the warming and moistening of the air drawn into the nasal cavity The foramina are openings in the skullThe front, or anterior, wall is thick skull bone;



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures




Paranasal Sinus Definition Location Anatomy Function Picture
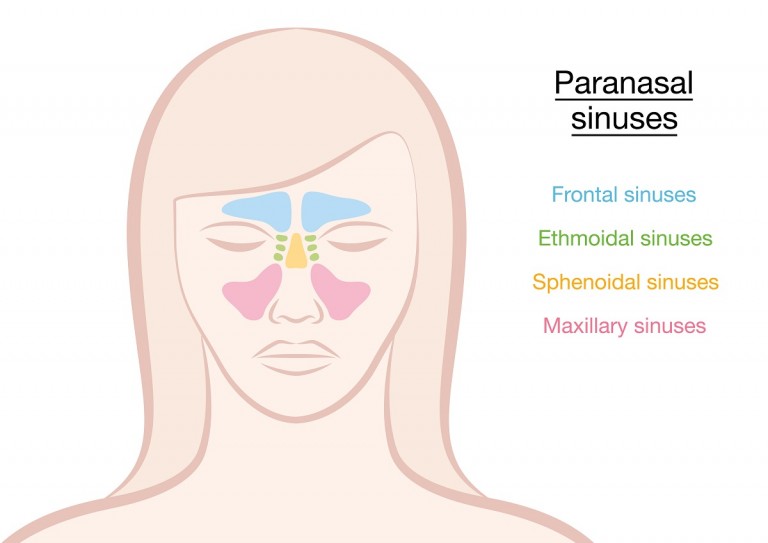
Paranasal sinuses Dr Sachintha Hapugoda and Dr Maxime StAmant et al The paranasal sinuses usually consist of four paired airfilled spaces They have several functions of which reducing the weight of the head is the most important Other functions are air humidification and aiding in voice resonance They are named for the facial bones inA Sinus or sinuses are hollow air cavities in the skull connecting the nasal passages They are connected via a narrow passageway called the ostium The sinuses purpose is to humidify the air to the lungs, as well as create mucus secretion to eliminate unwanted particles from the bodyReduce the weight of skull Provide resonance to the voice Contribute to facial growth Where Do Paranasal Air Sinuses Open?



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Physiology And Diseases Ppt Video Online Download




Paranasal Sinuses Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
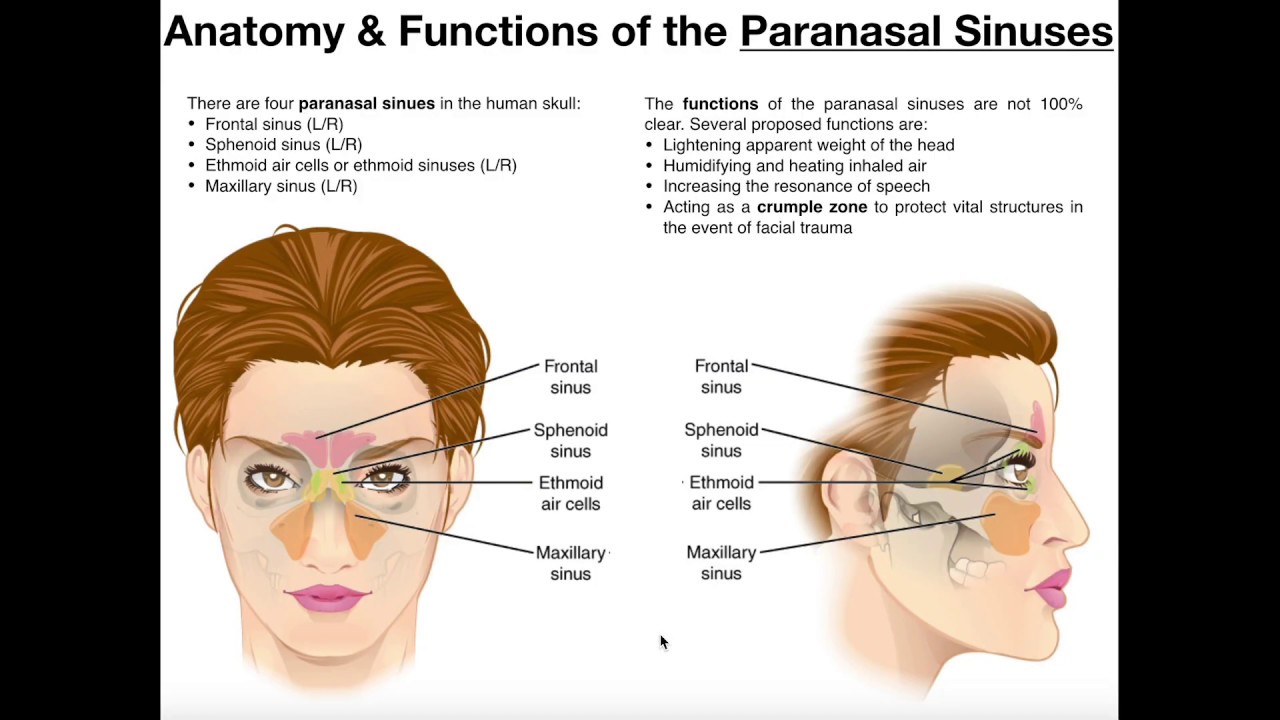
1115 · The functional reason for paranasal sinus presence has been discussed since the early descriptions of the sinuses in the 1800s Proposed functions have included voice resonance, humidification and warmth of inspired air, increase in olfactory membrane area, absorption of shock to the face and head, thermal insulation for the brain, lightening of the skull and facial bones, · Turbinates are a network of bones, vessels, and tissue that warms, humidifies, and filters the air the horse inhales In addition, seven airfilled sinus cavities called the paranasal sinuses17 · The sinuses are boneencased, airfilled spaces within the skull that communicate with the nasal cavity Species such as the horse have welldeveloped and distinct paranasal sinuses that include the frontal, dorsal conchal, ventral conchal, rostral maxillary, caudal maxillary, and sphenopalatine Species such as the dog have only frontal and maxillary sinuses Regardless, the paranasal sinuses




Sinus Anatomy Definition




Cancer Of The Nasal Vestibule Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Anterior Skull Base And Orbit Surgical Management Ento Key
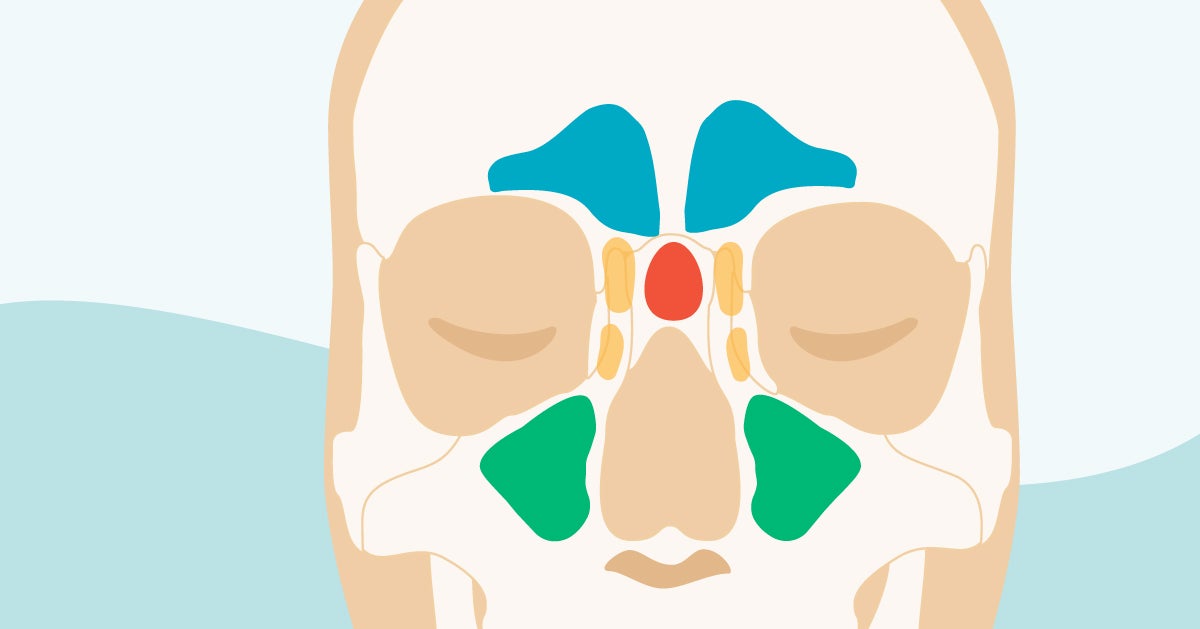
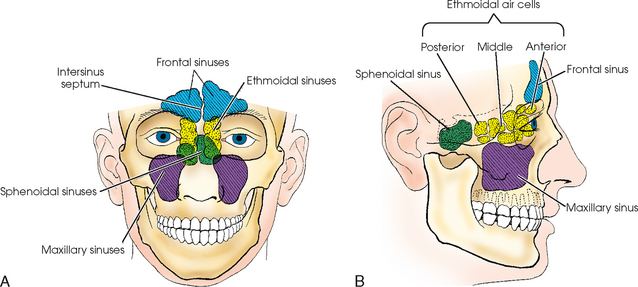
1300 · Skull Sinuses This image shows the position of the sinuses in the human skull Paranasal sinuses are a group of four, paired, airfilled spaces that surround the nasal cavity (maxillary sinuses), above the eyes (frontal sinuses), between the eyes (ethmoid sinuses), and behind the eyes (sphenoid sinuses)The paranasal sinuses are airfilled cavities in the skull There are four different sinuses (Fig 2) maxillary sinus; · The sinuses are a connected system of hollow cavities in the skull The largest sinus cavities are about an inch across Others are much smaller




Frontal Sinus Wikipedia



Are Your Sinuses Healthy Is Mold The Culprit Philadelphia Integrative Medicine
Paranasal sinuses The paranasal sinuses are airfilled cavities in the skull There are four different sinuses maxillary sinus ethmoid sinus sphenoid sinus frontal sinus To open class CT sinus, just click on the right side of the screen on CT sinus under the section TechniquesAir in cavernous sinus following peripheral venous access procedure Bone reconstruction of head CT in a patient with head trauma and skull base fractures shows a mastoid airfluid level in the left temporal bone Source image from a CTA in the same patient shows epidural air around the left transverse sinus The dural venous sinuses are intact without evidence for associatedThe frontal sinuses are above the eyes;



Anterior Cranial Fossa Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key



2
Cavernous sinus gas locules can be seen in several settings iatrogenic pneumocephalus secondary to gas embolism (especially venous gas embolism) from IV access (can be a relatively common finding in the absence of direct trauma and does not require treatment); · Functions of Paranasal air sinuses Make the inspired air moist and warm; · The sinuses are hollow spaces in the skull and the face bones around your nose There are four pairs of sinuses, named for the bones that they're located in The maxillary sinuses



Identify The Paranasal Sinuses Do Not Chegg Com




Nose And Sinus Anatomy Dr Thomas S Higgins Md Msph
· "The usual treatment is to get rid of the air and then seal the defect in the skull," Pouratian said It's something like a bicycle with a flat tire, only instead of pumping airBehind the sinuses lies bone covering the brain, and the floor of the sinuses slopes toward their openings into the nose The maxillary sinuses are not only the largest of the air sinuses but also the first to appear, being present inAll the paranasal air sinuses open into the nasal cavity Frontal air sinus (1 on each side) – Hiatus semilunaris (middle meatus)
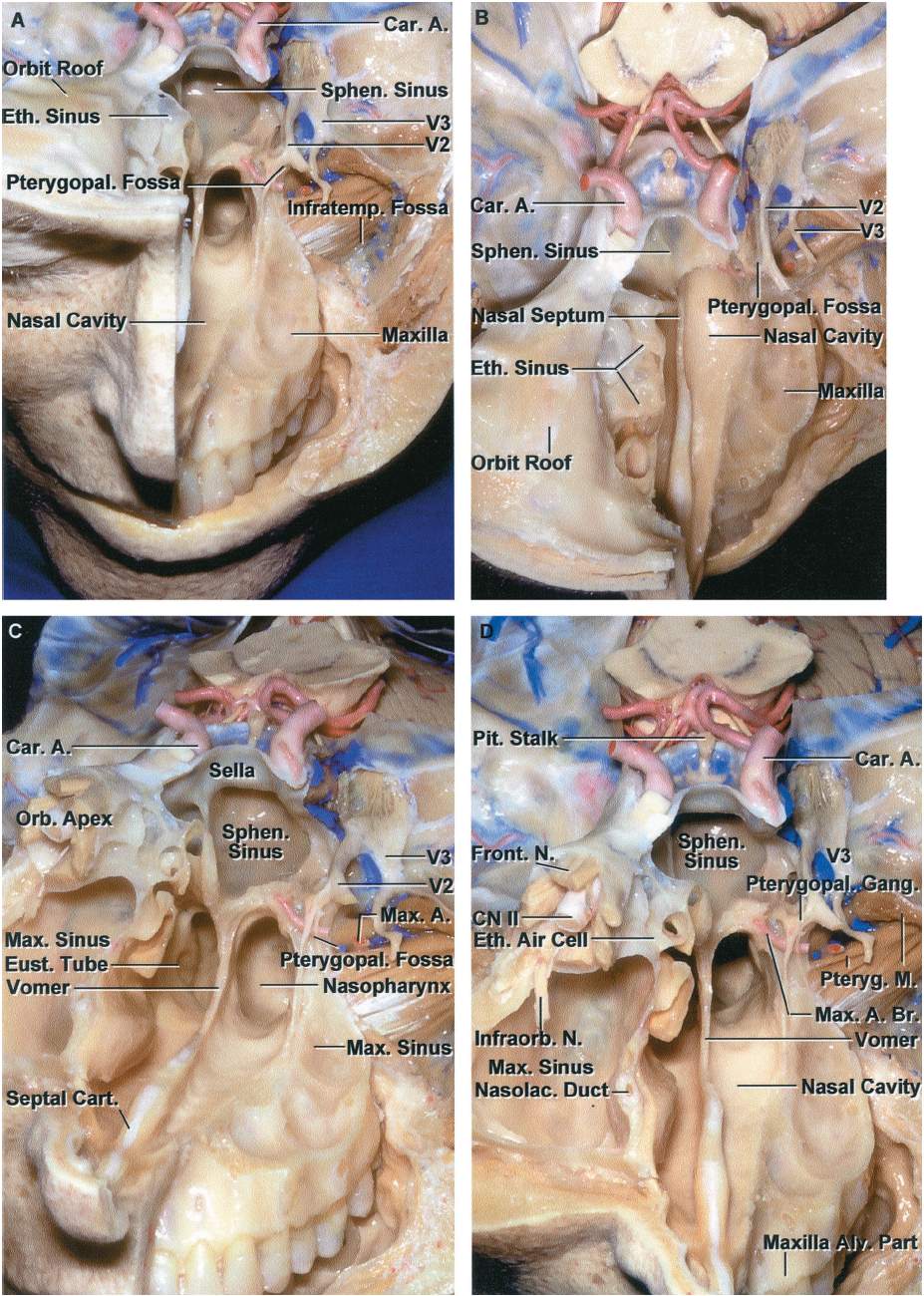



Anterior And Middle Cranial Base Neuroanatomy The Neurosurgical Atlas
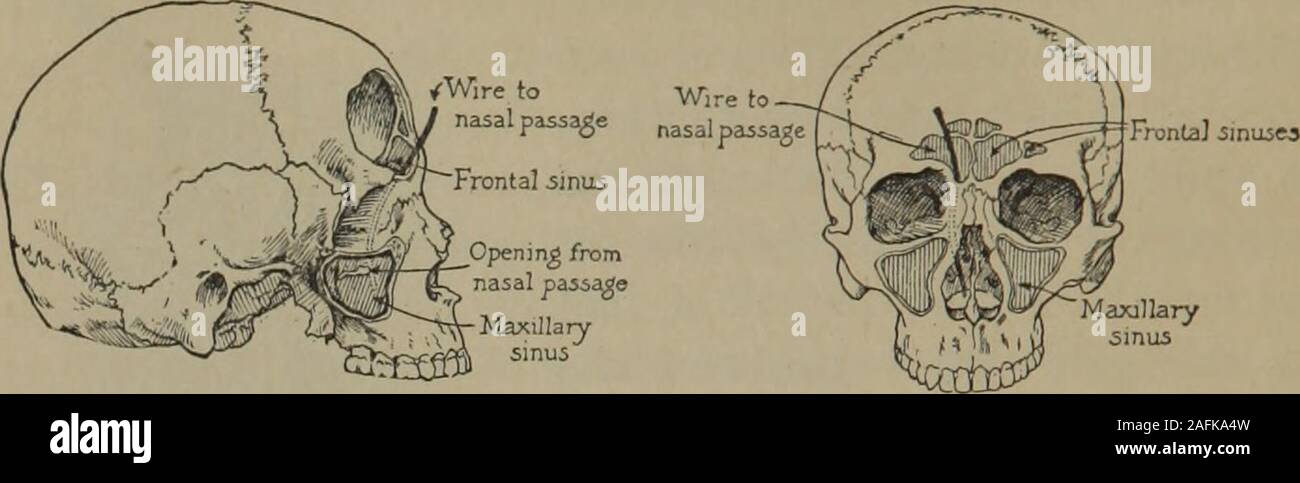



Personal Hygiene And Home Nursing A Practical Text For Girls And Women For Home And School Use Sing Bones And Is Thus Warmed And Cleansed Of Its Dust In The
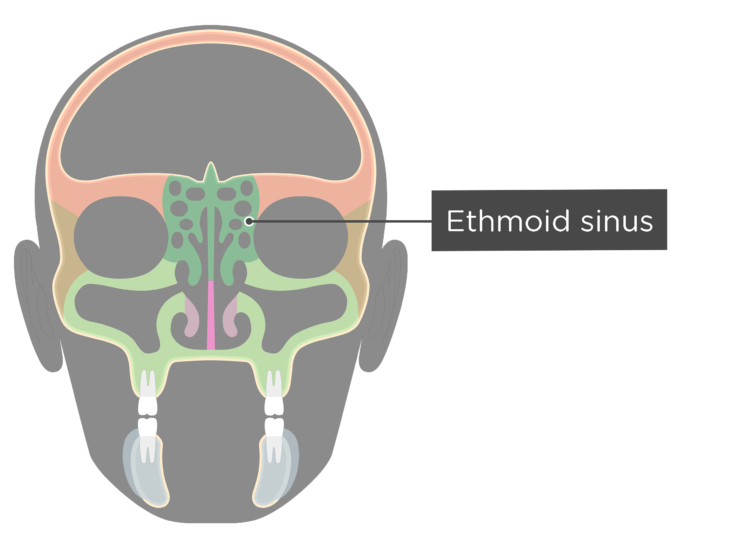
Ethmoid sinus (known as ethmoidal airWhat is the function of air sinuses in the skull?Skull fractures were not a constant finding in trauma patients with cavernous sinus gas CONCLU SIONS In patients without symptoms referable to the cavernous sinus, gas in the cavernous sinus does not appear to be a significant finding The gas is most likely the result of venous air emboli from intravenous lines or penetrating trauma Index terms Cavernous sinus, computed




What Are Sinuses Dr Joseph B Jacobs New York City Nyu Langone Medical Center




Pin On Anatomy
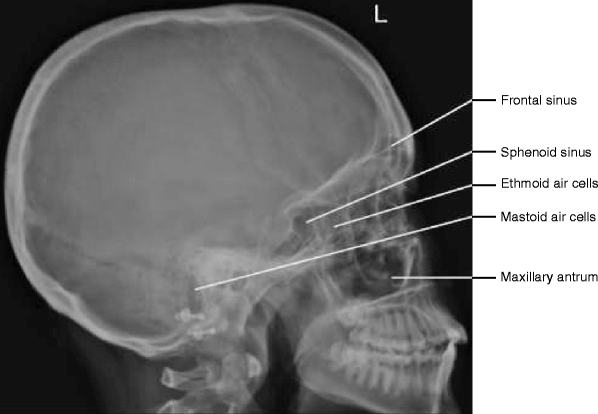
· There are four pairs of sinuses, which are spaces normally filled with air in the front of the skull over the eyes in the brow area; · The skull contains air sinuses which are highly variable in appearance between different individuals Sinuses CT brain (bone windows) Hover on/off image to show/hide findings Tap on/off image to show/hide findings Click image to align with top of page Sinuses CT brain (bone windows) The sphenoid sinus and ethmoid air cells are continuous with the nasal airways;The airfilled chambers found in several bones of the skull are called B Sinuses Sinuses help add resonance to the voice making it travel further and also help lighten the skull
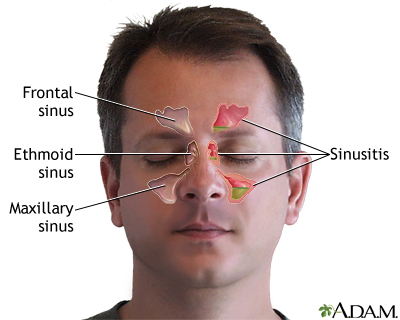



Sinusitis Information Mount Sinai New York




Nose And Sinuses Amboss
Truth be told, sinuses are nothing, but air cavities in our skull Imagine getting scolded for a hole! · Air within the cavernous sinus resulting from fracture of the wall of the sphenoid sinus was identified by cranial CT in a patient with head injury Careful search of the skullThe ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located




Paranasal Sinuses




What Is Nasal Cavity Nose Cancer What Is Sinus Cancer
The paranasal sinuses (latin sinus paranasales) are four bilateral airfilled spaces within bones of the skull surrounding the nasal cavityFour bones of the skull each accommodates a pair of paranasal sinuses that are named according to the bone in which they are locatedThe four sinuses are maxillary sinus,;Let's have a look on anatomical models and a human skull and see if we can fin The paranasal air sinuses often cause pain or discomfort if they get infectedThey are used to moisturize, and purify the air that we breathe Simply put, the air we breathe is not that suitable for respiration, courtesy of the pollution that has been increasing since the first EVS book mentioned it They help us breathe, and live Interestingly, whatever keeps us



Definition Of Paranasal Sinus Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Physiology And Diseases Ppt Video Online Download
Figure 2 Schematic anatomy of the sinuses The sinuses can be subdivided into two groups, depending where they drain into The anterior ethmoid cells, the frontal sinus and maxillary sinus drain into the middle meatus The posterior ethmoid cells and sphenoid sinus · Nostrils are the first walkway into your nose in the direction of the sinuses The air and other particles enter through this way The partition between that divides the nose in half is called the septum The nasal cavities inside the nose contain the entry to the sinuses Sinus Anatomy – Four Pairs of Sinuses Human beings have four pairs of sinuses Around 10% don't develop




Evaluation Of The Patient With Nasal And Pharyngeal Disorders Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Merck Manuals Professional Edition
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10270/Paranasal_Sinuses.png)



Schwannoma Of The Nasal Cavity Clinical Case Diagnosis Kenhub



Understanding Sinus Congestion Howstuffworks




E Book 02 The Skull Paranasal Sinuses



Los Angeles Ent Doctor Beverly Hills Sinus Surgeons



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures



2



Paranasal Air Sinuses Location Functions Relations And Applied Anatomy Qa
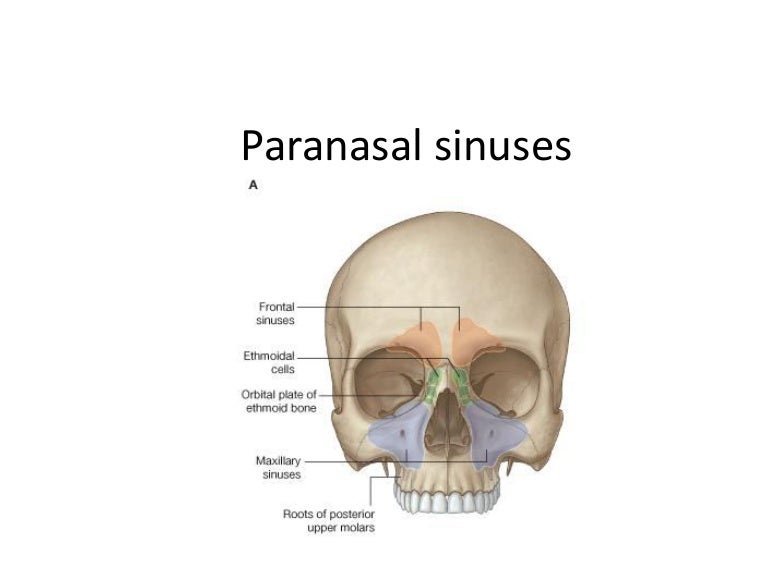



Paranasal Sinuses



The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway And Related Structures American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Anatomy Head And Neck Sinus Function And Development Article
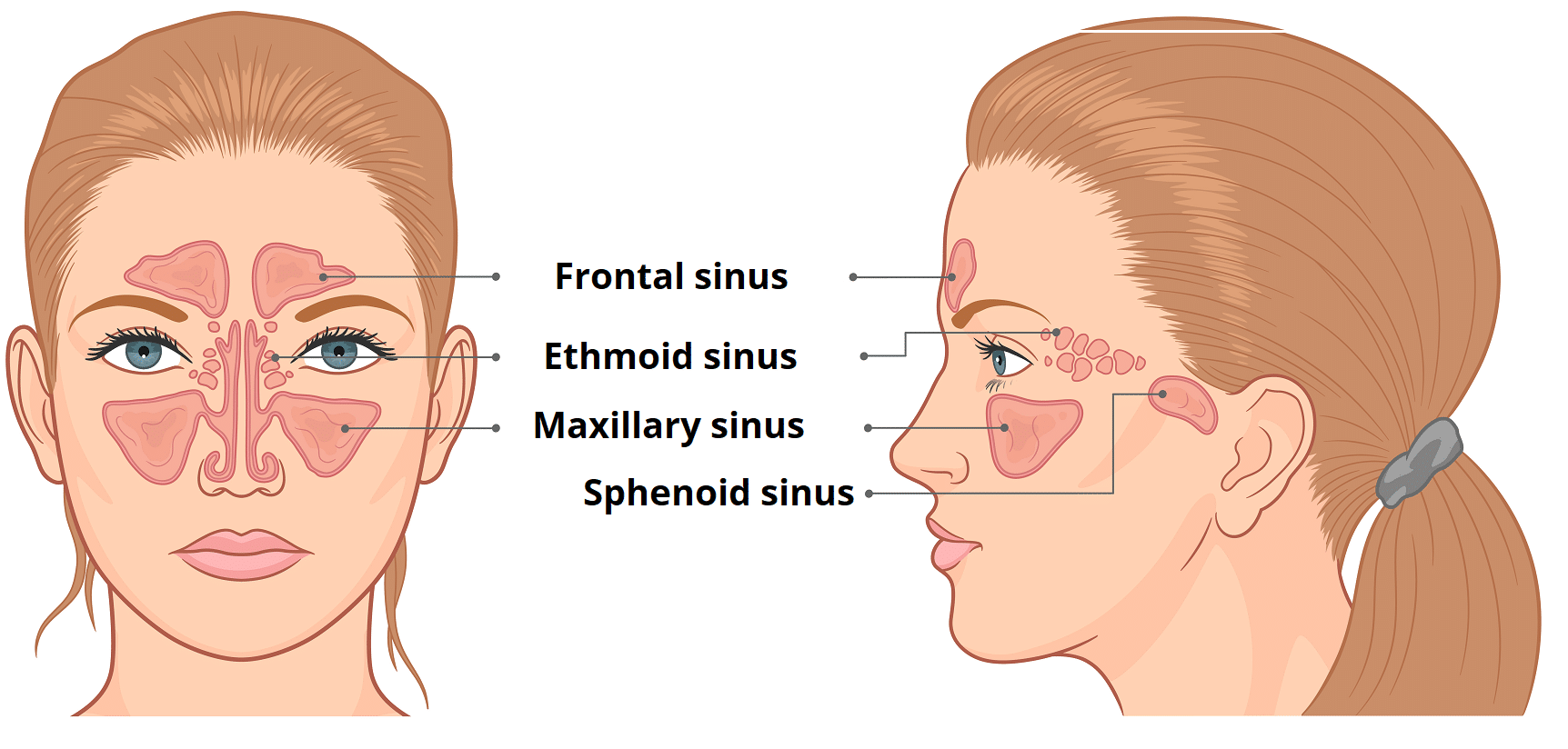



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy




Sinusitis Cancer Therapy Advisor




Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
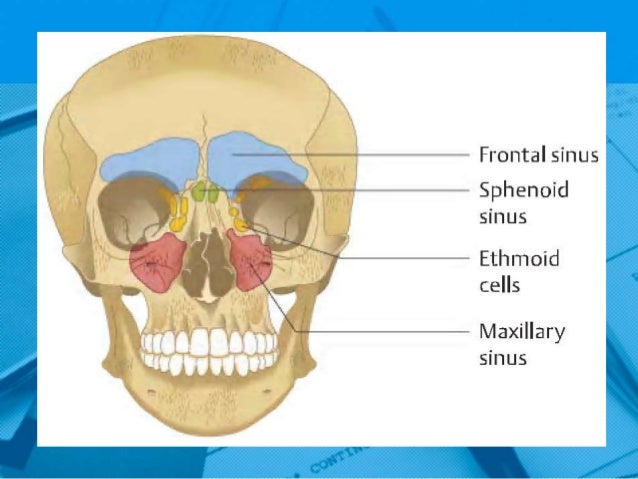



Anatomy And Physiology Paranasal Sinuses




Sinusitis And Sinus Infection Ent In Manhattan Ny Richard Nass M D




9 Nasal Cavity Ideas Nasal Cavity Anatomy Sinus Cavities



Frontal Sinus Fracture Posterior Table




Sinuses What Are They And What Do They Do My Sinusitis



2




Cancer Of The Nasal Vestibule Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Anterior Skull Base And Orbit Surgical Management Ento Key
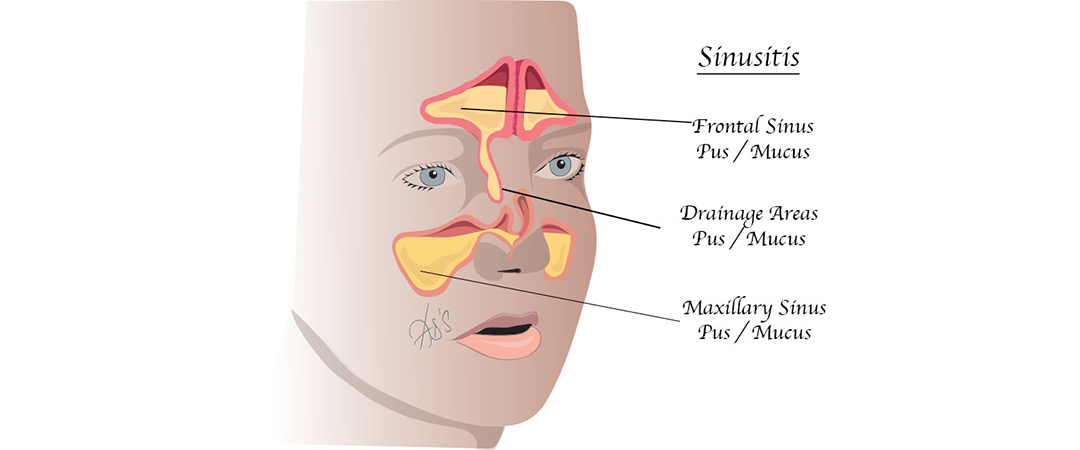



London Ent Associates Sinusitis And Sinus Surgery



Why Does My Whole Head Hurt When My Sinuses Are Congested




Paranasal Sinuses



Paranasal Sinuses The Paranasal Sinuses Are Chegg Com



Paranasal Sinuses Springerlink




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia



1



Sinusitis Sinus Infection Symtoms Causes Treatment For Sinus Doconline




Paranasal Sinuses And Sinusitis




7 1g Paranasal Sinuses Medicine Libretexts




Sinusitiserr




Paranasal Air Sinuses Youtube




What Are Sinuses Anatomy Types Study Com



Paranasal Sinus




Sinus Skull Anatomy Youtube




Startradiology




The Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Canadian Cancer Society



Paranasal Sinuses




What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities




Sphenoid Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




Location Of Paranasal Sinuses Download Scientific Diagram




Which Of These Skull Bones Does Not Contain A Paranasal Sinus A Frontal B Parietal C Maxillary D Ethmoid E Sphenoid Study Com



Sinus Barotrauma Divers Alert Network




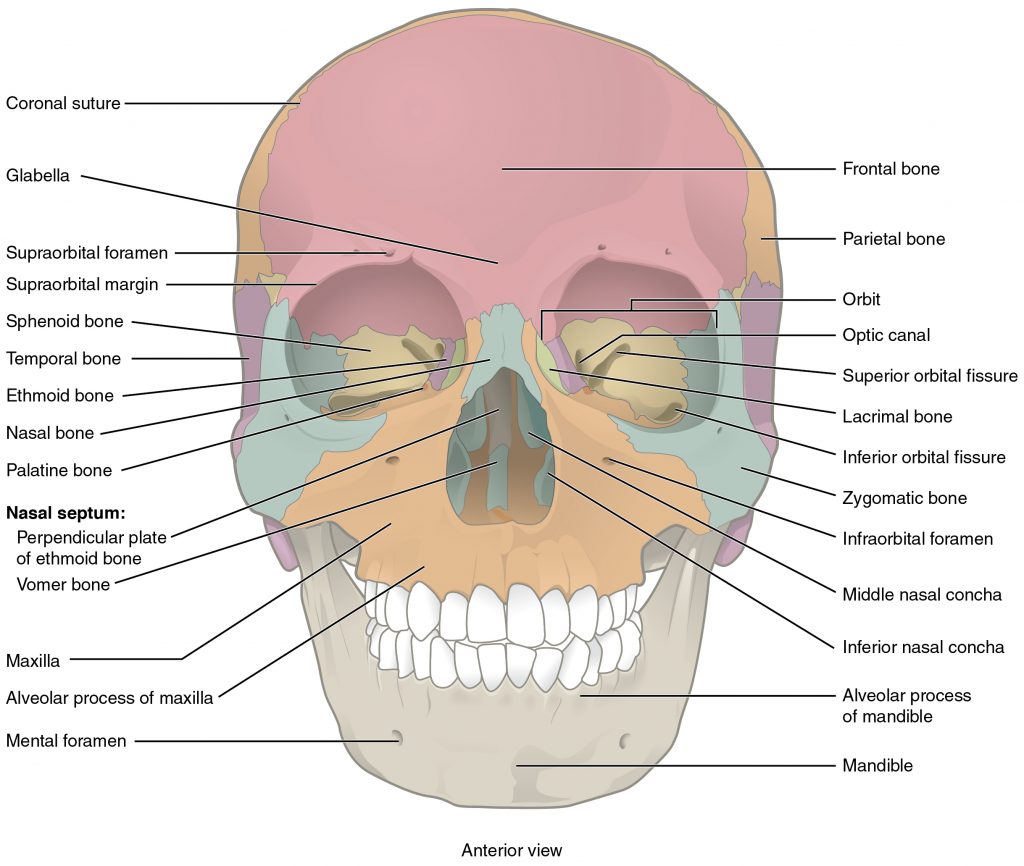
The Skull Boundless Anatomy And Physiology



Conditions Indepth Sinusitis Western New York Urology Associates Llc




Skull Scalp And Superficial Face




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia




Paranasal Sinuses The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




What Are The Sinuses Ny Center For Sinus Relief




Patient Resource Publishing Head And Neck Sinus Nasal




Location Of Sinuses In Skull Download Scientific Diagram



Epos C 2117



Paranasal Sinuses Human Anatomy Organs




Paranasal Sinuses Flashcards Quizlet



Anatomy And Functions Of The Paranasal Sinuses Youtube



Nose And Paranasal Sinuses



What Is The Significance Of Absent Frontal Sinuses Does This Hinder The Way Sinuses Are Supposed To Work What Effect Does Missing Frontal Sinus Have On A Person Quora




Skull Skeleton
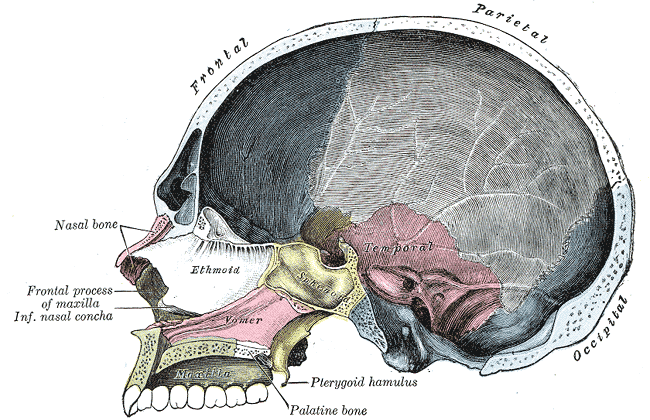



Sinus Cavities Paranasal Sinuses Location Anatomy Pictures Healthhype Com




Sinus Infection Bronchitis South County Internal Medicine
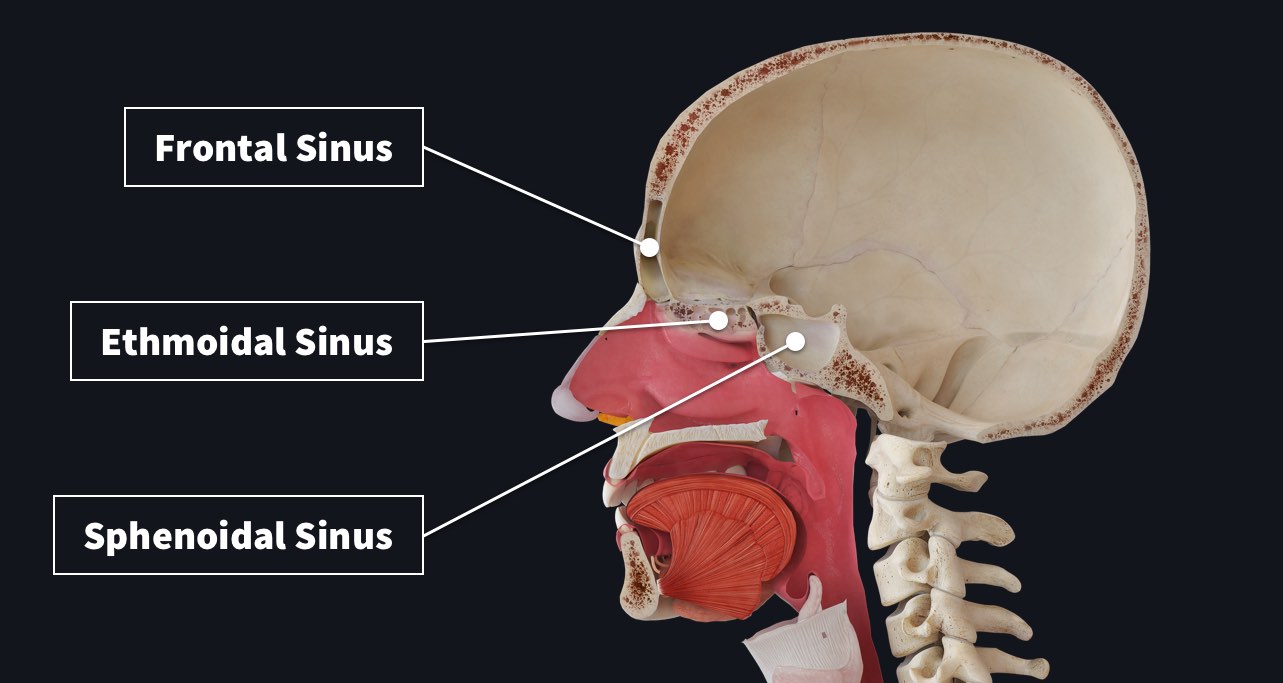



Paranasal Sinuses Complete Anatomy




Nose And Sinuses Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version




Sinuses Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
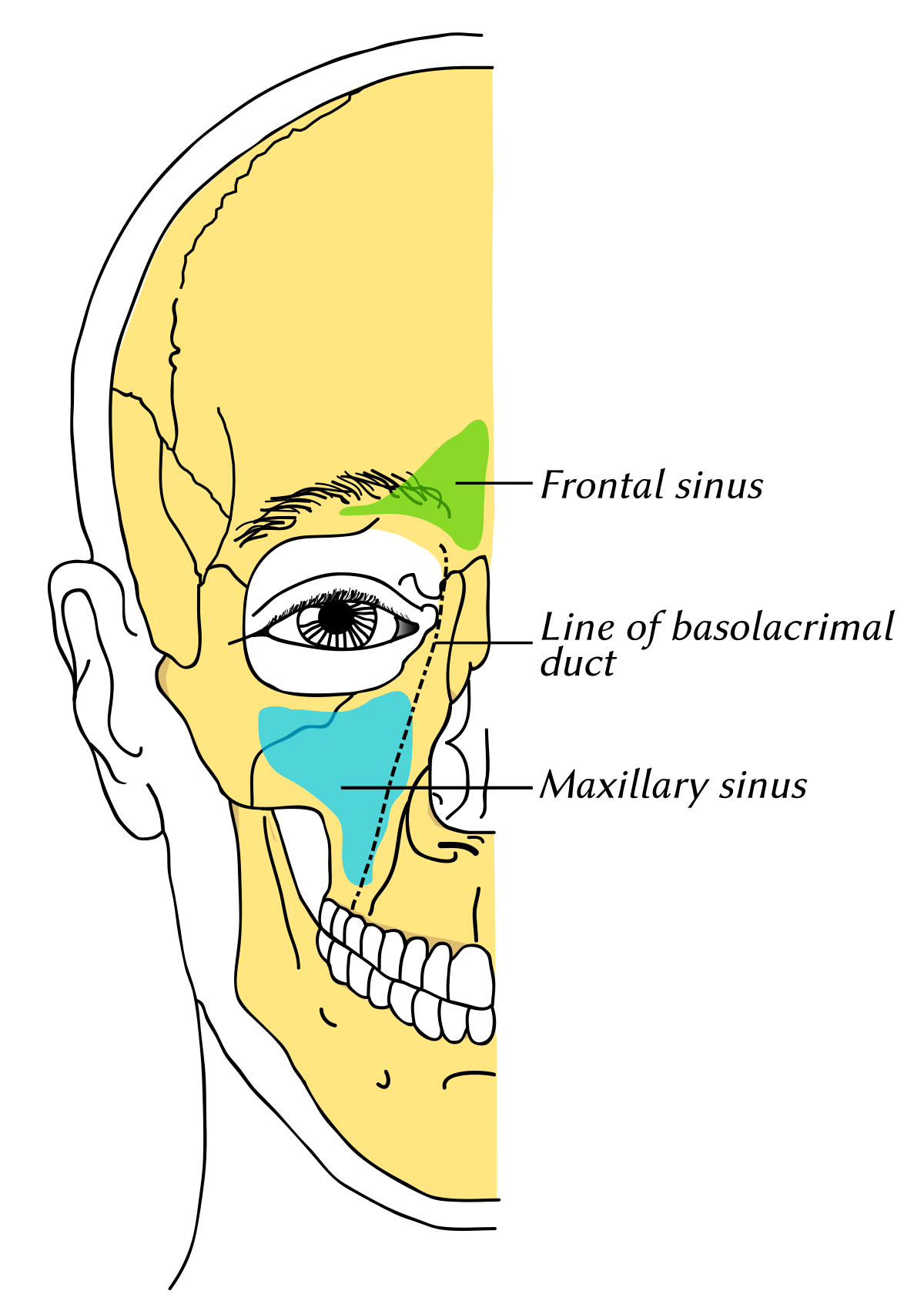



Frontal Sinus Wikipedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-paranasal-sinuses/972PC0nYOzlz7wqSgLmNA_sinus_frontalis_large_u9Vfozc0uUoMtc6KtIaUfw.png)



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
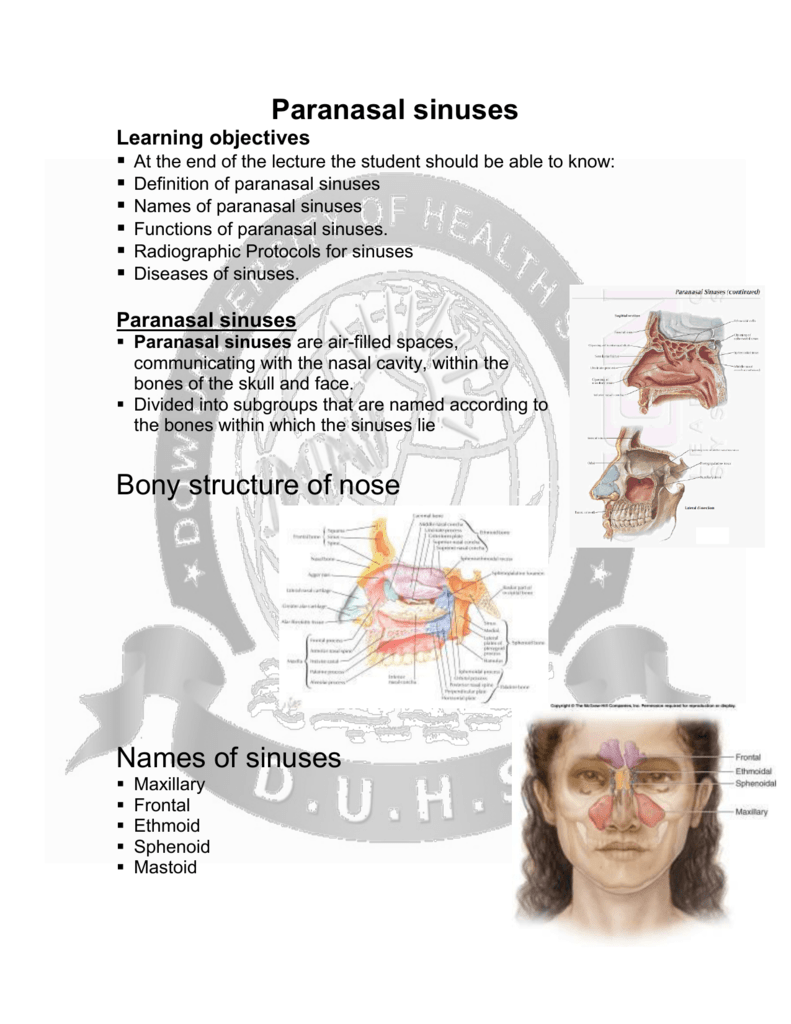



Function Of Paranasal Sinuses



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key



3




Cancer Of The Nasal Vestibule Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Anterior Skull Base And Orbit Surgical Management Ento Key




How To Tell If You Ve Got A Sinus Infection Stuff Co Nz




What Is The Ethmoidal Bulla With Pictures



1



7 2 Head And Neck Basic Concepts Nursing Skills




Pin On School




Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Flashcards Quizlet


コメント
コメントを投稿